Automating API deployment of API Gateway (Finale)
A Lambda-backed custom resource for AWS API Gateway API Deployment using CloudFormation
Want to catch up from the start? Click here to read the first part of the series
Previously...
In my previous article, I figured out the manual steps of provisioning an AWS API Gateway and API deployments via awscli.
Today's Objective
In this article, I will be creating the Lambda-backed Custom Resource that will be triggered when an update is detected in a CloudFormation changeset.
TL;DR
Learning Points
It is important to draw the line between provisioning and subsequent deployment of resources when using Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
In our case of using CloudFormation to provision and deploy AWS API Gateway, creating a new API deployment may not be most suitable via native CloudFormation.
A Lambda-backed custom resource to perform an API invocation to update the deployment may be a more suitable solution for retaining the deployment history and documentation version.
I agree with the response provided by the user
Federicoin this Stack Overflow post. Do give it a read!
TLDR; Source Code
Please ensure you fulfil the following prerequisites:
You have an existing S3 bucket with versioning enabled
You have an API JSON file with multiple versions
You can use the sample API JSON files here.
Remember to rename
api-full.jsontoapi.jsonwhen uploading to replace theapi.jsonfile in the S3 bucket
An update changeset will be detected by the CloudFormation stack, due to the changes for the following parameters
RestApiFileVersion: Version of the API JSON file
StageNameToUpdate: Target stage to deploy the new version of API to
SemanticVersion: Semantic versioning for the APIs
You can download the CloudFormation template from this repository
You can read through the CloudFormation template at your own pace and get your hands dirty!
You can always refer back to this article for more explanation
If you find this Lambda-backed custom resource too much to digest, try referring to this article which uses a much simpler use case
Walkthrough
In this section, we will focus on creating the required resources for the Lambda-backed custom resource.
Lambda execution IAM role
Lambda function
CloudFormation Custom Resource that will trigger the Lambda function
Lambda execution IAM role
The IAM role created in this snippet will have the following permission: - The IAM role can be assumed by AWS Lambda - Can pipe logs to AWS CloudWatch - Can create and update elements in AWS Gateway except for DELETE operations
LambdaExecutionRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- lambda.amazonaws.com
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Path: "/"
Policies:
- PolicyName: CustomResourceLambdaExecutionPolicy
PolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- logs:CreateLogGroup
- logs:CreateLogStream
- logs:PutLogEvents
Resource: arn:aws:logs:*:*:*
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- apigateway:POST
- apigateway:GET
- apigateway:PUT
- apigateway:PATCH
Resource: "*"
Lambda function
The Lambda function consists of
cfn_sendfunction to send the response back to the CloudFormation.- The function took reference from
cfnresponse, do refer to AWS official documentation on it
- The function took reference from
lambda_handlerfunction to perform the API invocation for API deployment
import json, urllib3, boto3
http = urllib3.PoolManager()
SUCCESS = "SUCCESS"
FAILED = "FAILED"
# cfn_send function has been exclude here for brevity
def lambda_handler(event, context):
response = ""
try:
apigw = boto3.client('apigateway')
rest_api_id = event["ResourceProperties"]["RestApiId"]
deployment_description = event["ResourceProperties"]["DeployDesc"]
stage_name = event["ResourceProperties"]["StageName"]
semantic_versioning = event["ResourceProperties"]["SemanticVersion"]
if stage_name == 'NA':
# Don't deploy the API that's updated in stage
cfn_send(event, context, SUCCESS, {})
else:
# Deploy API by creating deployment
response = apigw.create_deployment(
restApiId=rest_api_id,
description=deployment_description,
stageName=stage_name
)
# Update documentation version by creating new documentation version
apigw.create_documentation_version(
restApiId=rest_api_id,
documentationVersion=semantic_versioning,
stageName=stage_name,
description=deployment_description
)
cfn_send(event, context, SUCCESS, response)
except Exception as err:
print(f'{err}')
cfn_send(event, context, FAILED, response)
CloudFormation Custom Resource
The custom resource will invoke the Lambda function for each create and update changeset in the CloudFormation Stack.
DeployApi:
Type: Custom::ApiGWDeploymentFunction
Properties:
ServiceToken: !GetAtt ApiGWDeploymentFunction.Arn
RestApiId: !If [ CreateApiGateway, !Ref MyApiGateway, !Ref MyPrivateRestApiGateway]
DeployDesc: !Sub "Deploy API file ${RestApiFilename}, version id ${RestApiFileVersion}, semantic versioning ${SemanticVersion}"
StageName: !Ref StageNameToUpdate
SemanticVersion: !Ref SemanticVersion
Additional Notes
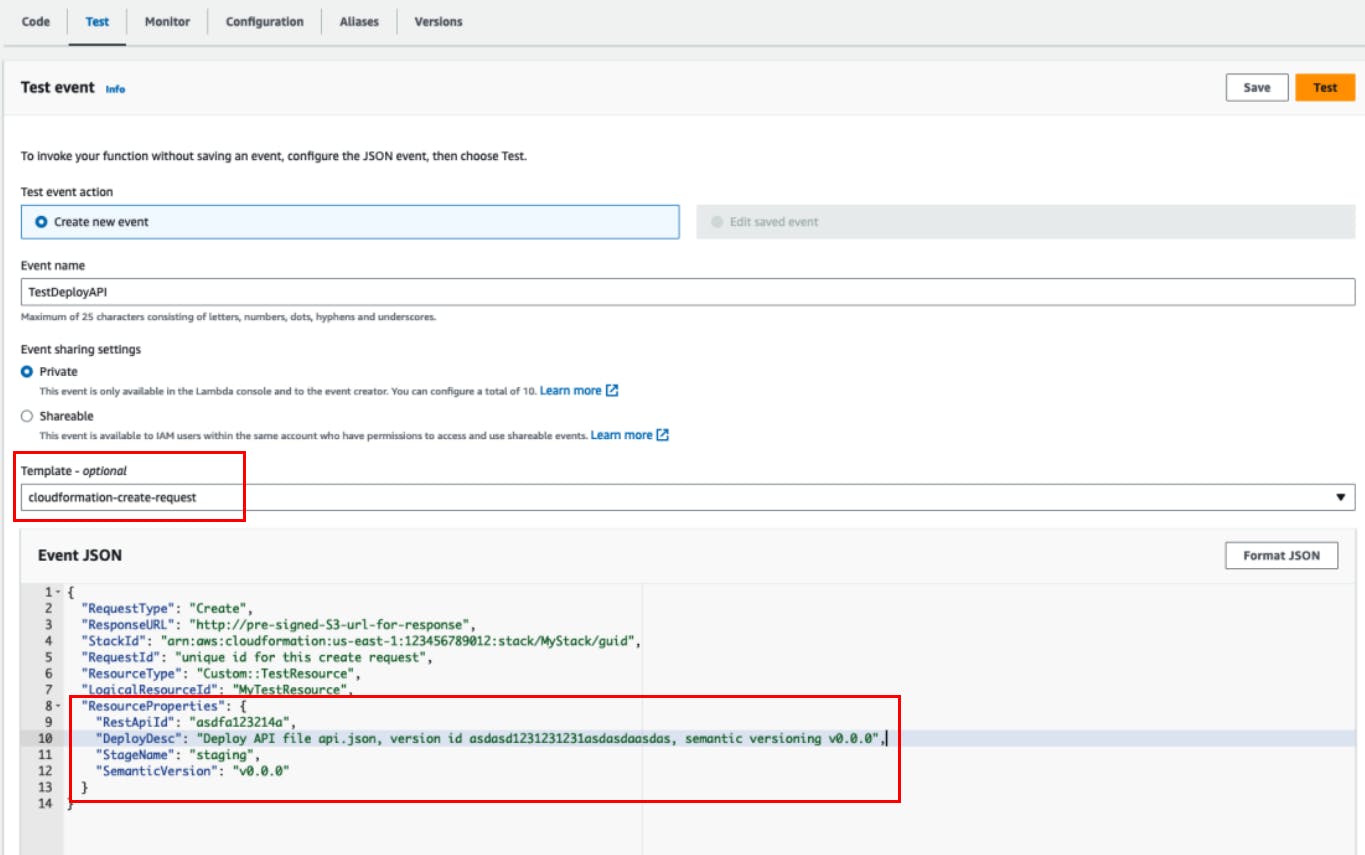
Testing inputs from CloudFormation to Lambda
To troubleshoot the Lambda function, you can use the cloudFormation-create-request template. You can include the parameter values under the ResourceProperties.
Further changes
Initially, I included the Documentation Version as part of the AWS resource.
DocumentVersion:
Type: AWS::ApiGateway::DocumentationVersion
Properties:
Description: "Documentation Version for ${RestApiFilename} Version ID: ${RestApiFileVersion}"
DocumentationVersion: !Ref RestApiFileVersion
RestApiId: !If [ CreateApiGateway, !Ref MyApiGateway, !Ref MyPrivateRestApiGateway]
However, I realised the Documentation Version was still being overwritten for the subsequent deployment. As such, I also included the creation as part of the API deployment Lambda function.
Considering that the documentation version can be any string, I decided to change it to use the semantic versioning rather than the S3 file version ID.
It would be easier to identify with and perhaps more meaningful in terms of versioning.
For the documentation description, I put it to be the same as the deployment description for illustration purposes.
# Lambda code snippet for creating documentation version
apigw = boto3.client('apigateway')
apigw.create_documentation_version(
restApiId=rest_api_id,
documentationVersion=semantic_versioning,
stageName=stage_name,
description=deployment_description
)
Execution Outcome
Overview
The following parameters will ensure there is an update changeset detected by the CloudFormation stack
RestApiFileVersion: Version of the API JSON file
StageNameToUpdate: Target stage to deploy the new version of API to
SemanticVersion: Semantic versioning for the APIs
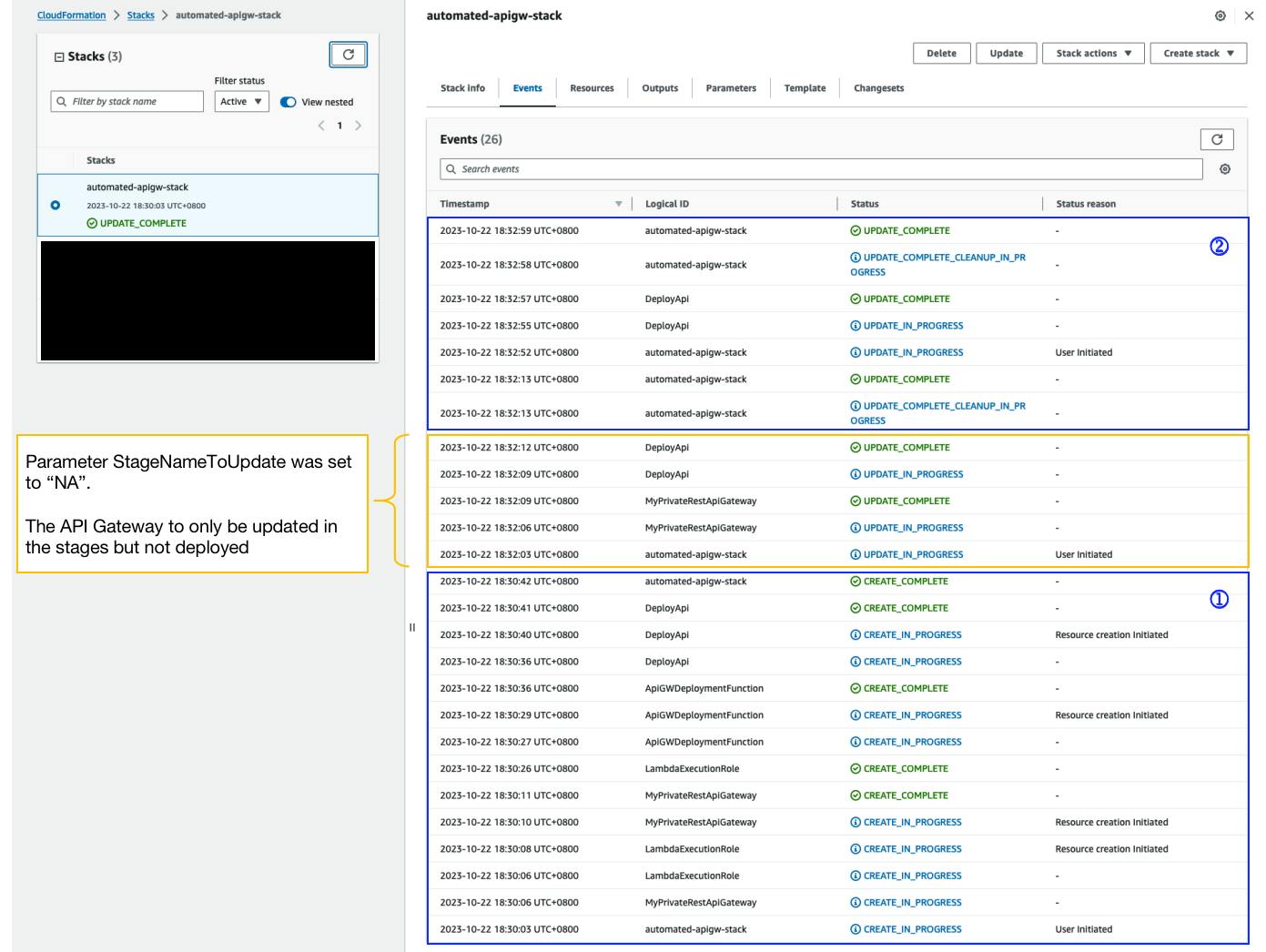
Results from the execution
In the Events section,
The successful API deployments are illustrated in blue boxes
The events annotated by the yellow box are an update to the API in the stages but not yet deployed
In the API Gateway Dashboard, we can see that the deployment history and documentation history are intact and not overwritten after the execution of update changesets in the CloudFormation Stack.
Documentation History
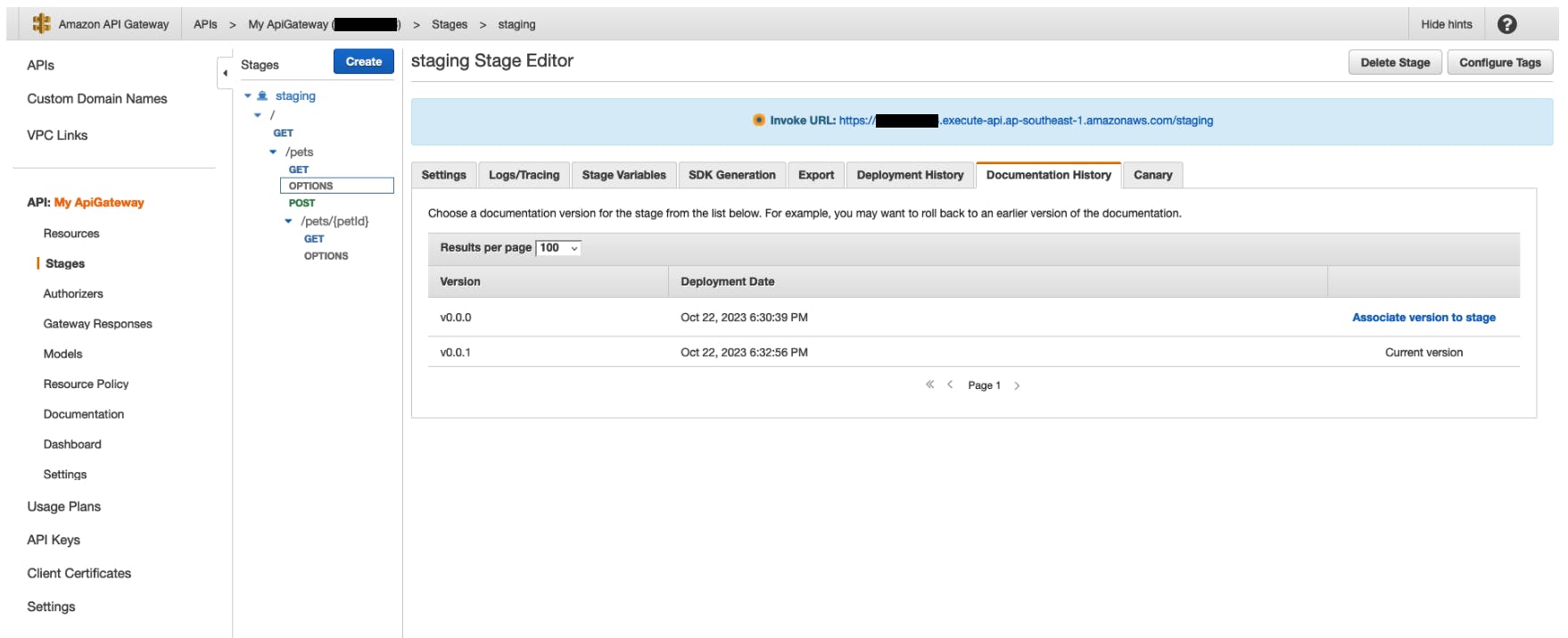
Deployment History

Considerations
The current CloudFormation template's design focuses mainly on the workflow and functionality of automating the API invocation for API deployment on API Gateway. Below are some customization considerations:
1. Scope of execution
The current IAM role is lenient and can be applied to any Lambda in your AWS account
You may want to reduce the scope of execution by limiting it to specific Lambda functions
2. Stage Name
In the current implementation, the Lambda function will create a new stage if the stage name doesn't exist.
If you want to limit the stage name, you can consider enforcing the allowed values in the CloudFormation parameters using
AllowedValues
StageNameToUpdate:
Type: String
Default: "staging"
Description: "To indicate recent stage that was deployed to. Indicate NA if you do not want to deploy the API for the changeset"
AllowedValues:
- "staging"
- "NA"
3. S3 File Version ID
Agreeably, using the S3 file version ID may not be intuitive as it will be hard to determine the versions of the API.
It may be wiser to name the
api.jsonwith the semantic version, e.g.api-${SEMANTIC-VERSION}.json.However, some manual effort is still required to retrieve the file's version ID. Since it is required as part of the CloudFormation API Gateway definition when using the
BodyS3Locationproperty.
4. End-to-End Process
The current implementation is only partially automated.
The API JSON file is manually uploaded
The CloudFormation stack still needs to be updated manually
Via S3 Event Notifications
Upon detecting a PUT event in S3 bucket, trigger the Lambda function to do an API deployment
In this case, a different implementation will be required to cater to a different event response for the Lambda function
Via CI/CD pipeline
The API JSON file is stored in a repository.
Depending on the pipeline CI/CD flow,
The API JSON file is uploaded to a version-enabled S3 bucket
Upon uploading, store the file's version ID and filename
Using the
awsclicommand, call the CloudFormationupdate-stackoption with the required values to update the CloudFormation stack and invoke the custom resource to trigger the API deployment
Final Thoughts
It's been one long ride to finally implement this Lambda-backed custom resource. Looking back, the problem statement may not be a complex one. Yet, it is surprisingly not easy to craft the solution 🙃
Glad to say I have learnt something new and understand how to implement Lambda-backed custom resources 🙌🏼
I hope this gives you a good peek into using Lambda-backed custom resources for API Gateway API deployment!